Setting up a Human Resources Information System(HRIS) is a crucial step for any organization wishing to optimize the management of its human resources. One of the most critical phases in this type of project is data recovery.
This process ensures continuity of operations and data integrity in the new system. It is therefore essential that it is well prepared and executed.
Data recovery in a nutshell
Data migration involves transferring information from an old system to a new one. This process includes the extraction, transformation and loading (ETL for Extract Transform Load) of data so that it is compatible and usable in the new HRIS.
A well-executed data transfer ensures that all the necessary information is available in the new system as soon as it goes live.
When should data recovery be planned?
It is essential to ensure that employee data is uploaded before the new HRIS goes live. This means that all employee information, such as personal data, compensation histories, performance appraisals and other critical information, must be available and verifiable in the new system before it goes live. This step minimizes interruptions and disruptions to day-to-day operations.
Tool compatibility, limits and constraints
It’s important to understand the limitations and constraints of themigration tool. Differences between the data structure of the old system (source) and that of the new system (target) are elements to watch out for.
This means :
- Identify potential incompatibilities between the two systems
- Plan any data transformations/transcodification required to adapt information to the new format
- Plan rigorous tests to ensure that migrated data is correct and complete (on different instances, for example).
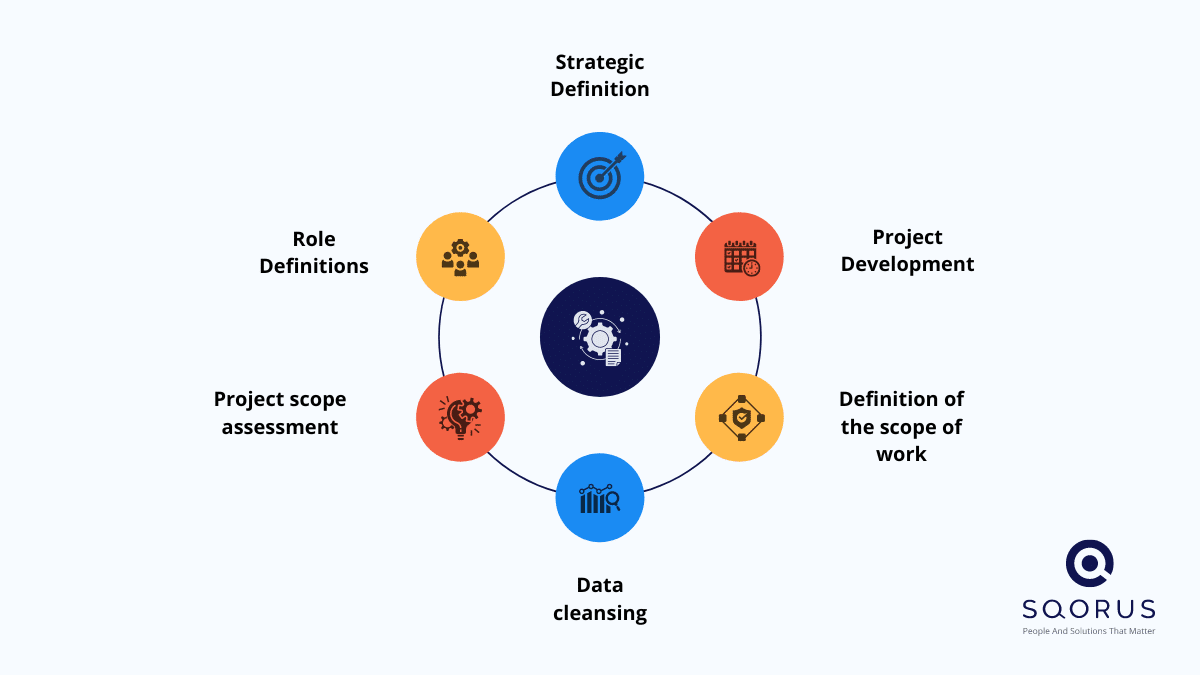
Preparing the data recovery project
A data recovery project requires meticulous preparation. The following pillars should be taken into account:
- Definition of the strategy: “big bang” data migration, migration in several batches… and inclusion of a freeze period for the old system, or consideration of a delta run if the old system continues to operate after the first load.
- Project development: schedule, number of runs/loading iterations, scope of each iteration, management of environments (pre-prod/prod/test for interfaces etc.).
- Definition of the scope and depth of the data to be recovered: which data (employment data, personal data, training catalog, organization repositories, candidates, etc.) and over what history (hiring and current line or 5-year history, etc.).
- Data cleansing: thanks to this data migration project, it may be worth seizing the opportunity to cleanse and update your data: eliminate duplicates, correct errors, archive obsolete information…
- Project scope assessment: assigning appropriate resources to both IT and business teams.
Ensure close collaboration between the two, and mutual understanding of needs and constraints.
- Definition of roles: define who does what, at what time, establish a precise RACI for the various stages of the data migration project: extraction, data cleansing, verification, validation for loading, loading, testing and release…) The RDD (data recovery) is a project in its own right within the overall project for implementing a new HRIS. The overall project schedule must take account of RDD planning.
Which data? What history? Which source(s)?
When preparing for data recovery, you need to determine the list of data to be migrated, and the depth of history required. This decision depends on the specific needs of the organization.
For example:
- Essential data: personal information, career events, remuneration history, etc.
- History depth: decide whether all historical data should be migrated or, for example, only data from the last five years.
- Reliable source(s): ensure that data comes from reliable, validated sources to avoid errors in the new system or data cleansing.
Data quality is crucial to the success of an RDD project.
Note that if data comes from multiple sources, this adds complexity to the project.
Verification and validation of uploaded data
The importance of verifying and validating uploaded data should not be underestimated.
It is imperative to :
- Perform load tests to check that data has been migrated correctly, and that the result in the new system is as expected.
- Compare source and target data to ensure that no information has been lost or corrupted.
- Involve end-users in validating data to confirm that it meets operational expectations.
Delta data management if 2 systems run in parallel
If the option is chosen not to freeze the first system and to let the two systems run in parallel, it’s essential to frame the phase properly to recover the delta of the data.
For this purpose, a :
- Data synchronization plan: set up mechanisms to synchronize new incoming data during migration.
- Contingency plan: provide solutions for handling data arriving during the migration phase, to avoid any loss of information.
- Transition plan: ensure a smooth transition from the old to the new system to minimize disruption to day-to-day operations through change management and user training on the new system, for example.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the success of a data recovery project depends largely on the careful preparation and rigorous execution of each stage of the process.
At SQORUS, we have developed expertise in this type of project, both in the technical aspects and in functional support. We have several customer references, notably onOracle HCM Cloud integration projects. By calling on our experts, you’ll be able to guarantee a smooth and seamless data migration, ensuring the success of your HRIS project.
Contact
A project? A request?A question?
Contact us today and find out how we can work together to make your company’s digital future a reality.













