What is the Workday integration platform ?
Workday is SaaS* software for managing human and financial resources.
Data is managed primarily through reports and data integration.
Workday Studio, which will be featured here, is a tool for creating complex data integrations for Workday. It’s a unified, Eclipse**-based environment for developing, deploying, and updating complex integrations, running in the Workday cloud.
Workday Studio is a perfect example of a low-code tool. Low code*** tool, where you can create assemblies of reusable blocks.
Integration source code is XML-based, but like an Eclipse module, Studio also supports Java customization.
Three Workday tools to build integrations
In Workday, there are three types of integrations – Cloud Connect, Enterprise Interface Builder and Workday Studio. Each has its own benefits and limitations.
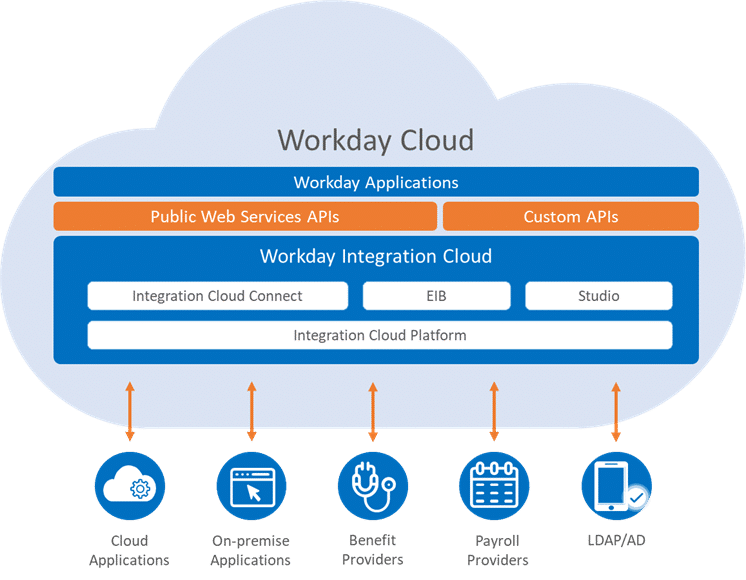
Workday’s first tool: Cloud Connect
The first type are Cloud Connect integrations.
These are standardized predefined integrations, called connectors, supported and maintained by Workday. There are a number of useful connectors for many use cases. They significantly reduce the development time needed to build a complete integration. Each connector is configurable to suit different needs.
The benefits of this approach are:
- Access to a set of predefined integrations;
- Low cost, low risk, and quick to deploy with no need to code;
- Integrations fully supported by Workday, certified and tested through regular updates and fixes.
These integration models should be the first choice when building new integrations, if the desired model exists. These integrations can then be enriched by data transformations or Studio integrations.
Workday’s second tool: Enterprise Interface Builder
The second type of integration is the Enterprise Interface Builder (EIB).
TheEIB tool provides an easy-to-use, guided graphical interface that allows integrations to be set up with little or no programming. This tool is used to create simple data input or output integrations. They constitute between 40 and 50% of all integrations used. Of these, up to 90% are outbound integrations and use Workday reports as data sources. However, ISBs are limited. Each integration supports only one data source and one transformation. ISBs are to be used to create low data volume and low complexity integrations.

Workday’s third tool: Workday Studio
Workday Studio, the third type, is used for other, often more complex integrations. It allows a great flexibility of creation. Generally, the following cases of using Studio can be cited:
- several data sources;
- efficient and scalable process;
- source control, unit tests, debugging… ;
- handling of complex errors, different reaction depending on conditions ;
- complex, logical loops, depending on external variables or dynamic data;
- large data sets to transfer.
Workday Studio: the most complete integration tool
- Workday Studio integrations are developed in distinct phases:
Design: building assemblies in Studio - Deployment: connect to the Cloud directory and deploy theintegration in Studio
- Configuration: configuration of services required by theStudio integration system, such as integration maps, transports, permissions or notifications, to be performed in theWorkday application
- Launch: launch the integration either from Studio or from theWorkday application
- Monitoring: track the progress of theintegration from within Workday Studio or the Workday application. It is also possible to access a consolidated report of the integration process once it is complete.
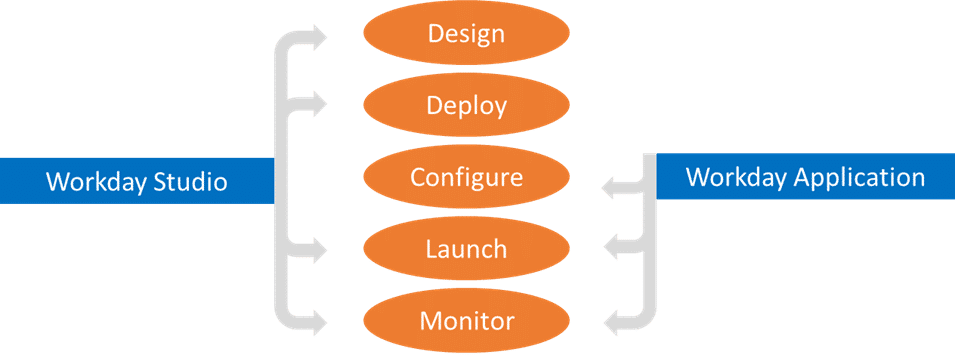
The design phase is the most time consuming, as it involves the entire construction of the integration. The following phases follow each other quite quickly.
Here are the different assembly tools presented below.
Workday Studio: API connection
One of the main resources of Workday Studio is the connection to Workday’s API****.
The first method of using Workday APIs is through web services and the SOAP protocol. Workday web services are used to collect and update data in Workday. Example: the Change Job web service allows you to change the assignment of a person. Studio provides the tools to configure, test and trigger web service requests. SOAP requests provide access to Workday data and are secured by Workday’s security protocol.
The second method ofusing Workday APIs is through Workday reports as data sources. This allows, thanks to the principle of RaaS (Report as a Service), to use Workday reports as web services. They can be called directly in the Studio integrations through REST requests.
The third method ofusing Workday APIs is a synchronous request/response transport that sends requests from Workday to a URL through an HTTP protocol. This can be done via SOAP or REST requests.
Workday Studio: using blocks
In Workday Studio, an integration is developed through an assembly using the Workday Studio visual assembly editor.
An assembly is a graphical representation of an integration system. It is composed of different configurable components (or blocks) each having a functionality: creation and manipulation of variables, format transformation, error handling, etc.
Individual components are linked together to form processing chains, and define integration. The outgoing message of each component becomes the input of the component to which it is connected. The assembly editor offers complete freedom on how to connect components together.
Elementary components provide a way to connect processing steps together in processing chains. Advanced components provide a way to dynamically control how assembly execution moves through the processing chain.
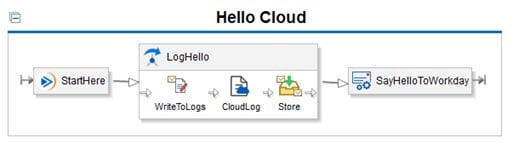
The assembly editor provides a wide range of components to manipulate messages and communicate with other systems through various protocols such as FTP, SFTP, SMTP (email), HTTP and HTTPS. The assembly editor also supports message transformations using XSLT (Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations). XSLT is a form of XML-to-Text mapping called Text Schema.
There are two representations of the assembly. The first is a graphical representation, displayed in the default Design tab. A Source tab also exists, and represents the XML source code of the integration. It is best to add and configure the assembly components using the editor, not directly by editing the XML components in the Source tab.
Once the assembly is completed and saved, it is deployed to Workday. Then the integration is launched by choosing the launch settings, either in Studio or in theWorkday application.
Assemblies provide a number of features to enable the creation of scalable integrations. All integrations must be developed in a scalable and adaptable manner. It must be assumed that the data sources they process can be arbitrarily large. For example, with each processing of item information, it should be assumed that the number of items can increase to an arbitrary number. The fundamental approach to ensuring that integrations are scalable is to use components called splitters and aggregators. They allow you to split the data source into individual records (e.g. one item).
These components are necessary to use. Indeed, as a SaaS* software, there is no direct access to the Workday database. It is therefore necessary to compensate with as many good optimization practices as possible. In addition, an integration will be stopped after four hours of treatment. So you need to be able to run integrations in less than four hours, even with large volumes of data.
Workday Studio: Error Control and Management
Integration events include a set of logs used for diagnosing errors in integrations. This includes the launch request, the server console log, and the performance profile log in CSV format. The consolidated report summarizes all this in XML format. It is available for ISBs and some connectors but is more useful for errors in Studio integrations.
These control elements can be found in Workday Studio as well as in theWorkday application.
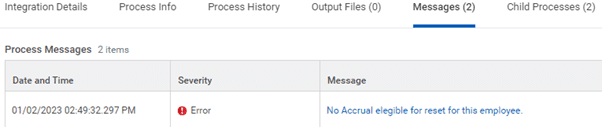
In addition, Workday Studio contains a debugger to detect and identify errors in a program. It allows you to visualize the execution of the program by placing breakpoints, which suspends the launched integration. By going step by step, it is possible to examine the content of the variables and thus find out where the errors come from.
Workday Studio : support
Workday Studio can be a difficult tool to grasp and use, especially without certification. There is not much content (on Stack Overflow for example) to help us. There are two main ways to find the answers to our questions, besides YouTube videos and trainings.
The first is Workday Community. It’s a collaborative space where you can :
- Post/read articles on best practices
- Find many solved problems, like Stack Overflow, on the forum
- Ask a question on the forum, if it does not already exist
- Ask a question directly to Workday support, who can provide answers individually, by answering the ticket, or by call
- Paying for Office Hours, which allows for an interview with Studio experts
The second is Help Contents. This is a section directly in Studio that gives some syntax and uses of functions.
Conclusion on data integration with Workday Studio
What I like most about Workday Studiois the diversity of the blocks, which bring together a wide range of functions. The freedom of use of these blocks allows you to create precise and complete integrations.
However, the handling of Studio is not completely intuitive, and the help is not complete enough on the internet, which requires many empirical tests. You also need to pay attention to the optimization of integrations, which requires the use of good practices and a good knowledge of Studio.
Don’t wait, contact us now to learn more about how we can help you get the most out of Workday Studio.
With SQORUS consultants, use Workday effectively and make informed decisions to achieve your goals.
* SaaS: Software as a Service = Application software solution hosted in the cloud
** Eclipse: IDE*** written in Java, now multi-language and multi-platform
*** Low code: Software development mode that hides all or part of the complexity of the application’s source code
**** API : Application Programming Interface = Software interface that allows to connect a software or a service to another software or service in order to exchange data and functionalities
***** IDE : Integrated Development Environment
All about IT project governance
Discover the roles and responsibilities of key profiles, as well as best practices in governance and technological development, to ensure the success of your digital transformation projects.
Also read in our "IT project governance" file:
- Lowcode platform: the future of application development?
- The use of UIPATH as an RPA solution
- Project comitology: the governance bodies of an IT project and their roles
- Steering and governance of a Finance IS project: which profiles should be involved?
- Steering and governance of an IT project: which profiles should be involved?
- Project governance: what role for the steering committee?
- The actors of a project team: organization, role and skills
- The IS manager at the heart of the development and evolution of systems
- HRIS Manager: what role in the evolution of HR Information Systems?
- IS project manager: what role and responsibility in an IS project?
- Functional consultant: a role close to the business processes
- Technical consultant: a profession at the heart of technological development
- Solution architect: a profession that manages development and deployment
- DevOps Consultant: role, missions and development skills
- Data Protection Officer (DPO): what roles and missions?
- CISO: a key job within the business for system security
- The service delivery manager at the heart of team management
- Scrum master, a key profession for Scrum project management
- Data scientist: a strategic profession at the service of management
- MOA / MOE: how are the roles divided on a project of implementation of an information system?
Contact
A project? A request?A question?
Contact us today and find out how we can work together to make your company’s digital future a reality.







