The reform of electronic invoicing, which requires companies to exchange invoices electronically, has seen the emergence of several types of player.
In this article, discover the different actors who will accompany the transition to e-invoicing reform and the key steps to prepare your company for the transition.
Between 2 and 2.5 billion invoices are exchanged each year in France. Electronic invoicing, also known as e-Invoice or e-Facture, is still too often seen as a simple paper invoice in image or PDF format.
Now, the French Finance Act has clarified its application framework, including the European standard EN16931, defining the semantic data model expected for an electronic invoice.
From 2024 onwards, only structured formats will be accepted, and PDF alone will gradually no longer be permitted.
With the reform, new solutions (PPF, PDP, OD) will be integrated into companies’ application ecosystems to cover theire-billing flows.
This being the case, new questions are emerging: Who are the new actors who will accompany the reform’s passage? How do you choose which of the various architectures is best suited to your business context? Quelles sont les étapes clés pour réussir sa transition vers ces nouveaux outils d’e-facturation ?
The Y-Scheme and the new reform players
To implement the new law on electronic invoicing, the tax authorities have modeled the incoming and outgoing invoice flows between buyers and suppliers in a “Y” diagram, using new tools.
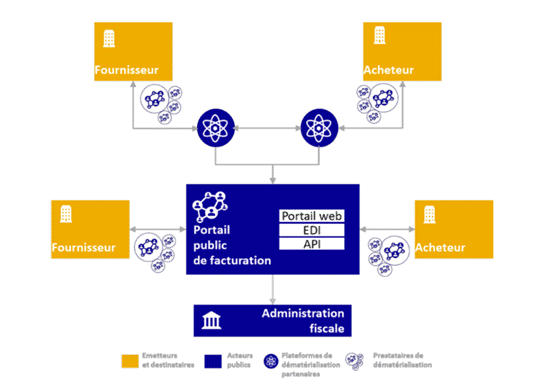
The Public Billing Portal
The “Portail Public de Facturation” (PPF) is a trusted public third party operating as a free service to centralize transactional and referential invoicing data for the tax authorities. In addition to this service, the PPF will take charge of the directory allowing, among other things, the registration of the various companies and their dematerialization platform(s).
The Partner Dematerialization Platform
A Partner Dematerialization Platform (PDP) is a private trustworthy third party offering mainly dematerialization services for incoming and outgoing invoicing flows. Its services will include complete management of P2P (Procure-to-Pay) and O2C (Order-to-Cash) flows. Les entreprises privées, optant pour une solution PDP, seront autorisées à échanger directement des flux de données de facturation entre elles. Vendors are required to be state-approved for their PDP solution. To date, no PDP has yet been recognized, with the official list scheduled for the first half of 2024.
A dematerialization provider or operator
A Dematerialization Provider or Operator “DPO” is also a private trusted third party that can offer the same type of services as a PDP. On the other hand, a company using an OD cannot directly exchange billing data with another company, but can exchange flows via the PPF. The DO is not required to obtain state certification to operate.
With the introduction of the new law on electronic invoicing, many questions are raised about the application of e-invoicing and e-reporting. In our previous article, discover the to help your company prepare for the challenges of these new regulations..
Functional contributions of the new solutions
Bien que les apports attendus par une solution puissent différencier d’une entreprise à une autre, nous vous proposons une liste non exhaustive de fonctionnalités potentielles, pouvant orienter le choix d’une solution d’e-facturation.
| PPF | PDP | OD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Principaux apports | |||
| Réception de factures directement du fournisseur via PDP | X | X | X |
| Consultation annuaire pour vérification du tiers (client, fournisseur) | X | X | X |
| Mise à jour de l’annuaire | X | X | X |
| Extraction des données à destination de la DGFIP | X | X | X Proscrit |
| Certifications ISO/IEC/27001 et SecNumCloud | X | X | X |
| Prise en charge du format Facture X, UBL (Universal Business Language), CII (Electronic Data Interchange) | X | X | X |
| Prise en charge de la facturation en masse | X | X | X |
| Edition des e-Reportings (B2C, B2B et B2G internationaux / B2C France,…) en conformité avec la norme | X | X | X |
| Conversion du format d’une facture éditée par un fournisseur ; en assurant l’intégrité, l’authenticité et l’exhaustivité des données | X Limité | X | X |
| Authentification : niveau de sécurité fort | X | X | X |
| Intégration système de signature électronique | X | X | X |
| Intégration avec principaux ERP du marché (On-premise, SaaS, PaaS, IaaS) | X | X | X |
| Autres services : Couvertures des cycles achats et ventes de bout en bout, Authentification SSO, Workflows d’approbation, Espaces collaboratifs , Dashboards avec KPI’s personnalisables, Moteur à base d’IA | X | X | X |
Depending on their needs and the level of maturity of their application and functional ecosystems, companies will have more or less strong expectations from the various players. The cost of implementing the solution is not likely to be the only criterion for choosing a solution.
Indeed, since all solutions operate in SaaS with the provision of services, their choice will then have to consider the expected levels of depth and performance of the developed functionalities, as well as the “hidden” costs (licenses, maintenance, training, archiving, storage, etc.) inherent to this type of solution.
Prepare for the shift to these new tools
Since the 90’s, digitization and associated technologies have revolutionized the economic world by offering a new paradigm on document management for both companies and individuals. What’s more, the advent of e-commerce has made it inevitable for companies to move towards paperless invoicing.
The reform only regulated an already well-established practice, allowing, among other things, better traceability and authentication of economic transactions. However, there are still heterogeneous levels of maturity, irrespective of company size, in order to align processes and information systems with the challenges of the reform.
Therefore, the preparation of the choice of its solution(s) appears clearly as one of the keystones necessary to the success of its transition to the reform for companies.
Analyzing existing systems is a key activity, and one that needs to be carried out as far upstream as possible in the selection phase, both in terms of processes and the technical-functional specificities of information systems. The work should not focus solely on supplier and customer invoicing. In fact, work sites will have to be parallelized on P2P and O2C flows, with an end-to-end vision, in order to :
- evaluate the level of capitalization resulting from its existing ;
- Challenge the different editors on the adequacy of their standards with the specificities of the company (sectorial standards, …);
- respond to the challenges inherent to the necessary change management, in order to limit the impacts related to the superposition of new specific layers;
- Secure the different levels necessary for the choice and deployment of a solution.
Au-delà du dimensionnement des moyens humains et budgétaires, la Gouvernance projet doit être clairement identifiée auprès des différentes parties prenantes (Sponsor, MOA, Intégration, Business, …) afin d’éviter tout risque d’inertie.
Since the tools are developed in SaaS, the editors very often keep the control of the integration of their solution. Therefore, depending on the framework (Agile – Scrum, V-cycle or mixed) desired for the project, this can have a strong impact on the project governance.
An AMOA and management system must be defined prior to the selection phase, and then shared transparently with the publishers, in order to :
- to align the positions between the customer and the integrator with an independent body;
- make relations between the various parties more fluid and manageable;
- to facilitate decision making;
- secure traceability of decisions ;
- to allow the control of the planning, given the restricted deadlines of the “0 buffer” reform.
Finally, although data cleansing is an integral part of every IT project, it is even more important when it comes to dematerializing invoices.
Indeed, since the editors have a billing model based largely on the archiving, storage and processing of documents, it is necessary to take advantage of this project to secure the perimeter of transactional data recovery as well as referential data on all impacted processes. This allows, among other things, to:
- Challenge the publishers on the costs of archiving and storing the invoices;
- avoid the tunnel effect for business teams, among others, in case of juxtaposition of other activities (accounting closing, …);
- anticipate the feasibility and technical complexity of aligning old data with the requirements of the reform…
How to anticipate the issues and challenges of the new e-invoicing reform for your company? In a previous article, you’ll find all the information you need to know in order to prepare your company’s ecosystem and make the transition to e-billing reform
Conclusion on the different actors of the e-bill reform
En conclusion, le choix d’une solution, qu’elle soit PDP, PPF seul ou OD, sera propre aux besoins de chaque entreprise. Notwithstanding their specific characteristics, companies will need to adopt a “quick wins” approach to standardizing their customer and supplier invoicing processes, in order to demonstrate their agility in the face of future technological and regulatory changes posed bye-invoicing.
New trends are likely to emerge among publishers positioning themselves on the e-invoicing market. Many of them are now positioning themselves on sectoral niches (e.g. jefacture.com for accountants) or are opting for strategic partnerships with ERP publishers (e.g. Esker with Cegid). In the face of competition, publishers will be expected to upgrade their service offering, with P2P or O2C pure players now developing functionalities for both streams.
SQORUS, a Council specialized in the digital transformation of HR, Finance and IT functions, can help you with your e-invoicing issues. Do not hesitate to contact us to discuss this with our experts.
Digital transformation of the Finance function : how to identify growth opportunities?
Discover how Finance's digital transformation can optimize your company's performance, and effectively identify opportunities for growth.
Also read about the digital transformation of finance functions
- The obligation of electronic invoicing and e-reporting
- Electronic invoicing reform: what you need to know
- What is the role of the finance department today?
- 5 obstacles to the digital transformation of finance functions
- Improve financial processes with automation and RPA
- What changes does dematerialisation bring to the finance function?
- The finance function, an actor of change in the digital transformation of the company
- Predictive analytics to unlock value and detect growth opportunities
- Better managing talent to overcome the obstacles to digital transformation in the finance function
- Provide users with real-time data with data visualization
- Advanced financial analysis to improve decision support
- Identify the business processes in the finance function that would benefit most from digitization
- Security at the heart of the company's financial transformation
- From a Finance IS to a Finance Data System
- What are the key challenges facing finance managers today?
- What are the key regulatory issues for CFOs in 2023?
- Digitization of the finance function: what should we expect in the future?
- Finance management: what technological tools are available to CFOs?
Contact
A project? A request?A question?
Contact us today and find out how we can work together to make your company’s digital future a reality.





