Oracle Integration Cloud : 5 mistakes to avoid in order to improve your ecosystem
Oracle Integration Cloud is a comprehensive integration platform that combines robustness and agility to meet the complex challenges facing organizations. However, even within this high-performance solution, errors can occur and compromise its potential. In this article, discover the common pitfalls to avoid and follow our advice on how to make the most of this technology.
Oracle Integration Cloud (OIC) is emerging as a complete integration platform, fusing robustness and agility to meet the complex demands of modern businesses. Despite its privileged position, it’s crucial to recognize that, even within the most powerful solutions, challenges can arise during implementation. Although it boasts robustness, OIC is not immune to common errors and pitfalls that can compromise its full potential during interface development. It is precisely on this note that we begin our exploration of OIC‘s anti-patterns.
In the sections to come, we’ll take a closer look at the typical mistakes to be avoided when using OIC, while providing you with tips and best practices for overcoming these obstacles. Get ready to deepen your understanding of OIC and discover how to maximize its effectiveness while avoiding the most common pitfalls. Note that most of these tips can also be applied to any type of data integration architecture with technologies other than OIC.
#1 OIC error: chatty integrations
And yes, even integrations can be chatty, and in a world where the loquacious is not always welcome, this can have serious consequences. To explain more concretely, a chatty integration is characterized by the fact that it interrogates a system in a unified way for several registrations. Take, for example, the case of an integration tasked with reading employee data from a database and updating this information in a third-party system via an API. Let’s imagine that the developer has opted for a user loop approach, calling the API individually for each user to update their data.
Wherever possible, this is NOT A GOOD PRACTICE and should be avoided at all costs. Successive calls to a system can overload it, impacting its behavior and leading to integration errors. OIC costs are also impacted, as this approach increases message consumption, which can quickly lead to credit overruns.
To solve this problem, it is often a good idea to maximize the amount of data sent per call. Many systems offer this option; Salesforce, for example, allows up to 200 records to be sent per call. Opting for the use of OIC adapters also offers the possibility of processing a large number of records per call.
#2 OIC error: endless processing using a loop
In large ecosystems, where the volume of data to be processed is frequently high, and where several files need to be read, developers sometimes opt to use a loop in the integration to process all the data per instance. However, this approach has significant repercussions. These integrations can run for several hours without reaching their conclusion, with implications for other integrations that can’t start if the queue is saturated. In addition, the process may stall after a few hours due to the limitations of the OIC Framework, notably the six-hour maximum duration for scheduled processes.
To avoid this stalling scenario, we recommend limiting the number of processes per instance, using OIC parameters to save the last files processed for future executions, or opting for recursive integration calls.
#3 OIC error: complex synchronous integrations
Synchronous integrations are designed to provide an immediate response when invoked. Adopting this design model for integrations intended to interact with several systems and involving numerous conditions, such as uncontrolled loops or large iterations, is irrelevant.
Indeed, the creation of a synchronous integration is based on the need for a rapid response. It’s important to note that this type of integration, also known as “app-driven integration”, is subject to a 5-minute time limit. After this time, theintegration returns an error.
The key to overcoming this constraint lies in a precise understanding of requirements and thoughtful integration modeling. Indeed, if the estimate indicates that synchronous integration is likely to exceed 2 minutes, it makes sense to opt for an asynchronous approach.
Example of an app-driven integration that’s a little too busy.
#4 OIC error: duplicate connectors in OIC
In projects involving several team members, the risk of creating several connectors pointing to the same system with the same identifiers is high. This practice is not recommended, as it has a significant impact on maintainability, making subsequent management complex and prone to potential problems.
To remedy this situation, it’s simply necessary to set up clear nomenclature rules, shared between the different teams, and to establish a verification process prior to the creation of a new connector. This ensures more efficient connector management.
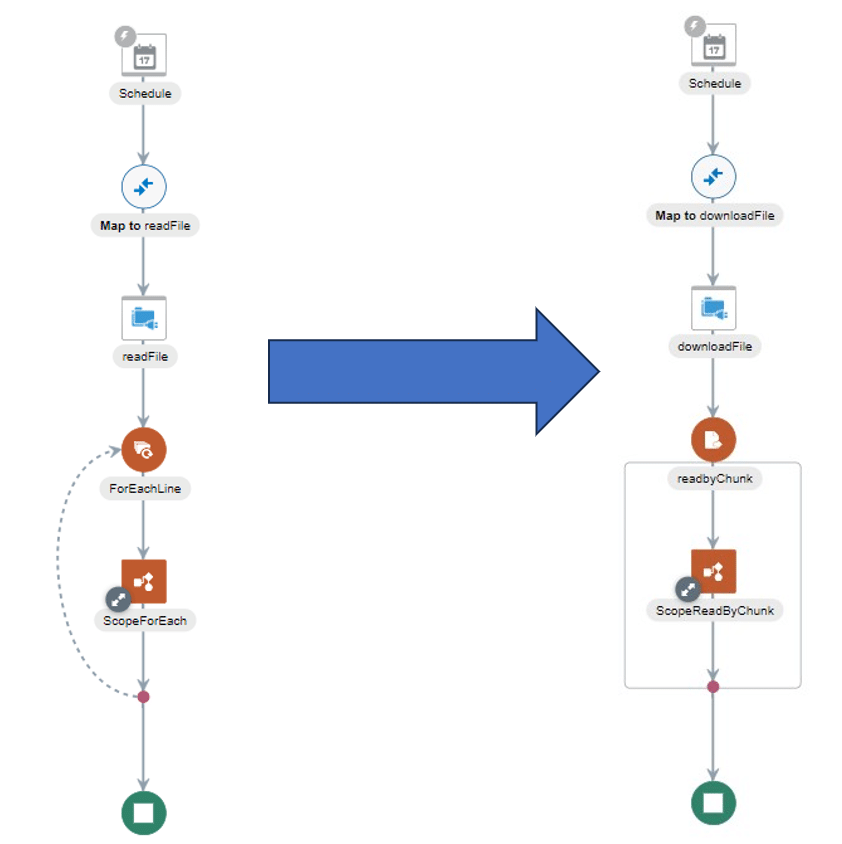
#5 OIC error: read files sequentially
In Oracle Integration Cloud, there are two distinct approaches to reading a file: full reading or reading in chunks (chunks).
The method commonly adopted by developers is sequential reading, which, although practical, can prove inefficient for large files, saturating memory by loading the entire file locally before reading it line by line. To optimize the scalability of your interfaces, we recommend segmented reading.
This approach enables more efficient competitive processing of files, offering greater capacity to manage large volumes of data.
Mistakes to avoid with Oracle Integration Cloud
In conclusion, navigating the Oracle Integration Cloud ecosystem requires a thorough understanding of anti-patterns and best practices in order to fully exploit the power of this integration platform.
The key lies in a thoughtful approach to design, careful modeling of integrations, optimization of processes, and respect for good naming practices. Avoiding the pitfalls of anti-patterns guarantees robust, high-performance, scalable integration.
By adopting this Council, developers can confidently navigate the complex world of OIC, maximizing the effectiveness of their integrations while avoiding common pitfalls.
Staying abreast of evolving best practices and continuing to refine integration strategies are essential to long-term success in deploying and managing Oracle Integration Cloud. If you need support in OIC expertise or data integration architecture, contact us today to discuss your specific needs and start optimizing your eco-system.
DOWNLOAD OUR FREE WHITE PAPER
” ALL ABOUT PROJECT GOVERNANCE IT “
Also read in our “IT project governance” file:
- Revolutionize your applications with the new APEX 23.2 features
- Simplify your validation processes with APEX 23.1
- The PMO, a role emerging with the transformation of organizations
- What new features does Oracle Integration Cloud Gen3 offer?
- How do you do complex integrations with Workday?
- Lowcode platform: the future of application development?
- The use of UIPATH as an RPA solution
- Project comitology: the governance bodies of an IT project and their roles
- Steering and governance of a Finance IS project: which profiles should be involved?
- Steering and governance of an IT project: which profiles should be involved?
- Project governance: what role for the steering committee?
- The actors of a project team: organization, role and skills
- The IS manager at the heart of the development and evolution of systems
- HRIS Manager: what role in the evolution of HR Information Systems?
- IS project manager: what role and responsibility in an IS project?
- Functional consultant: a role close to the business processes
- Technical consultant: a profession at the heart of technological development
- Solution architect: a profession that manages development and deployment
- DevOps Consultant: role, missions and development skills
- Data Protection Officer (DPO): what roles and missions?
- CISO: a key job within the business for system security
- The service delivery manager at the heart of team management
- Scrum master, a key profession for Scrum project management
- Data scientist: a strategic profession at the service of management
- MOA / MOE: how are the roles divided on a project of implementation of an information system?

